• Coughs can have various causes.
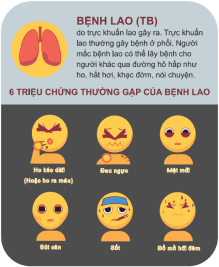
• If you have symptoms such as a prolonged cough, blood in your phlegm, low-grade fever, weight loss, or listlessness, it may be tuberculosis. In that case, you should be examined by a doctor immediately.
•If you have a fever or other symptoms that might suggest COVID-19, please contact the clinic or hospital in advance before visiting a clinic or hostpital.
COVID-19, influenza and tuberculosis both cause coughs, shortness of breath, fever, and listlessness.The biggest difference is the speed of progression of the disease. With tuberculosis, only one or two people for every ten people infected develop symptoms, and it often takes from several months to around two years for symptoms to become apparent.However, with COVID-19, symptoms start within a few days of infection. In both cases, once symptoms appear, be quick to get tested and be seen at a hospital.





 Comment
Comment Did this information help?
Did this information help?